Unraveling the Enigma of Elephant Rumbles: Nature's Infrasonic Symphony
Elephants, the gentle giants of the animal kingdom, have long captivated our imagination with their intelligence and social complexity. But beneath their thunderous footsteps lies a hidden world of communication that has only recently begun to be understood. These majestic creatures possess a remarkable ability to produce and perceive low-frequency sounds, known as infrasonic rumbles, that can travel for miles across vast landscapes. This fascinating aspect of elephant behavior has opened up new avenues of research and conservation efforts, shedding light on the intricate social lives of these magnificent animals.
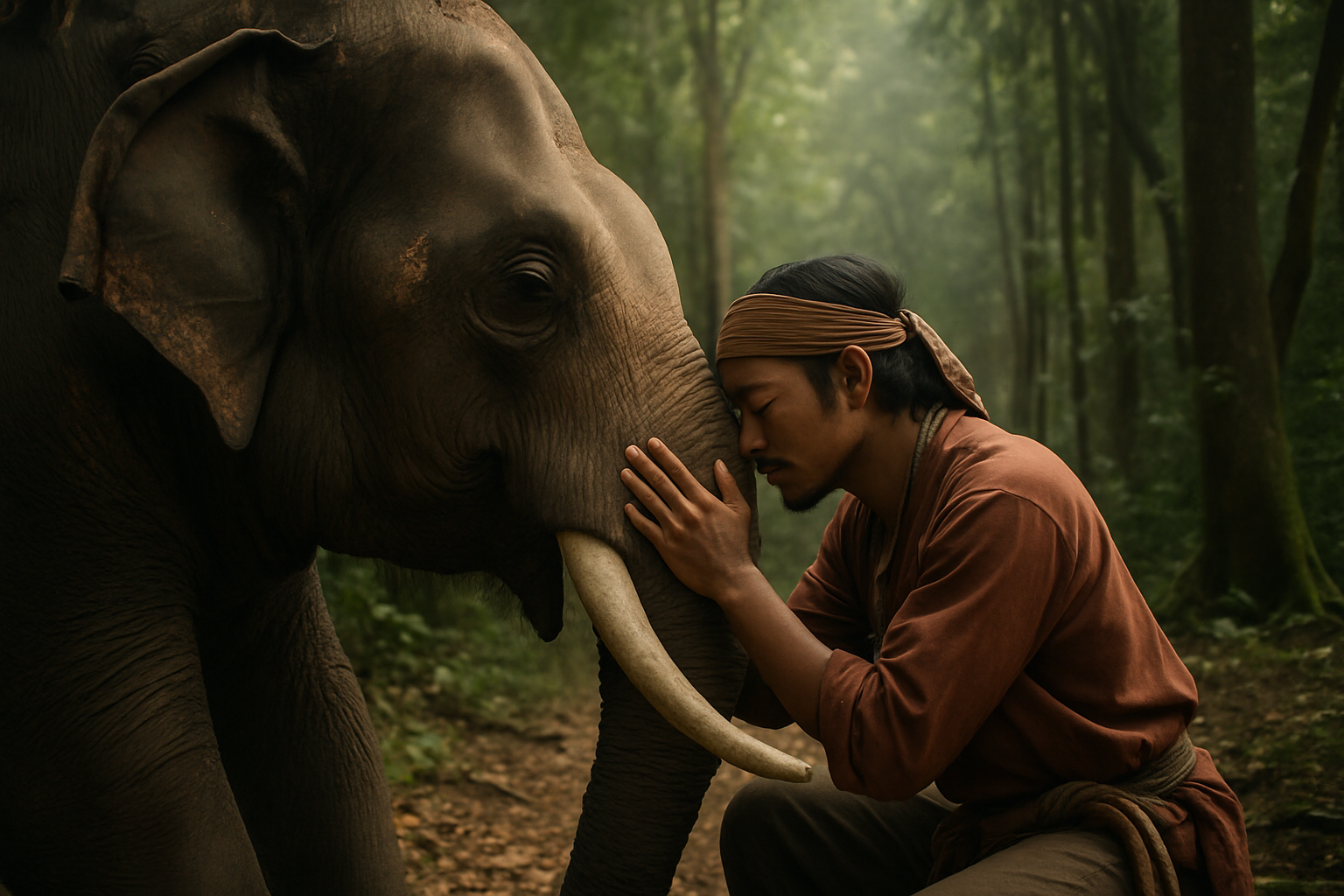

The Science Behind Elephant Rumbles
Elephant rumbles are low-frequency vocalizations that typically range from 1 to 20 Hz, well below the lower limit of human hearing at 20 Hz. These sounds are produced by the elephant’s larynx and are amplified by the massive nasal passages and trunk. The infrasonic nature of these vocalizations allows them to travel long distances, often up to several kilometers, with minimal attenuation.
Research has shown that elephants can detect these rumbles through various means, including bone conduction and specialized sensory cells in their feet. This multi-modal reception enhances their ability to pinpoint the source and direction of incoming signals, even in noisy environments.
The Language of Rumbles
Elephant rumbles serve a multitude of purposes in their social and environmental interactions. Studies have identified several distinct types of rumbles, each with its own acoustic properties and contextual meaning:
-
Contact calls: Used to maintain group cohesion and locate distant family members.
-
Mating calls: Produced by males in musth to attract females and assert dominance.
-
Alarm calls: Warn of potential dangers, such as predators or human threats.
-
Greeting rumbles: Exchanged when family groups reunite after periods of separation.
-
Foraging rumbles: Communicate the location of food sources to other group members.
By analyzing the frequency, duration, and harmonics of these rumbles, researchers have begun to decipher the complex language of elephants, revealing a level of sophistication previously unknown in non-human species.
Technological Advances in Elephant Acoustic Research
The study of elephant infrasound has been revolutionized by recent technological advancements. Specialized recording equipment capable of capturing low-frequency sounds has allowed researchers to eavesdrop on elephant conversations in their natural habitats. These recordings are then analyzed using advanced signal processing techniques and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and decode the semantic content of the rumbles.
One particularly exciting development is the creation of elephant-to-human translation devices. These prototype systems use artificial intelligence to interpret elephant vocalizations in real-time, potentially bridging the communication gap between humans and these intelligent creatures. While still in the early stages, this technology holds promise for enhancing our understanding of elephant behavior and improving conservation efforts.
Conservation Implications of Infrasonic Research
The discovery of elephant infrasound has had profound implications for conservation efforts. By understanding how elephants communicate over long distances, researchers have gained valuable insights into their movement patterns, social dynamics, and responses to environmental changes. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect elephant populations and their habitats.
One innovative application of this research is the development of early warning systems that detect elephant presence near human settlements. By deploying infrasound sensors along known elephant migration routes, conservationists can alert local communities to the approach of elephant herds, reducing human-elephant conflict and promoting coexistence.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant progress in understanding elephant infrasound, many challenges remain. The complexity of elephant vocalizations and the difficulty of conducting long-term studies in remote areas continue to pose obstacles for researchers. Additionally, the impact of human-generated noise pollution on elephant communication is a growing concern, as it may interfere with their ability to exchange vital information over long distances.
Looking ahead, scientists are exploring new frontiers in elephant acoustic research. Some are investigating the possibility of using infrasound to deter elephants from entering dangerous areas or to guide them along safe migration routes. Others are studying the potential therapeutic applications of elephant rumbles, inspired by the calming effect these low-frequency sounds seem to have on other elephants.
As our understanding of elephant infrasound deepens, so too does our appreciation for the intricate social lives of these remarkable animals. The hidden world of elephant rumbles serves as a powerful reminder of the complexity and wonder of the natural world, inspiring us to redouble our efforts to protect and preserve these magnificent creatures for generations to come.