The Role of Materials Science in Vehicle Construction
Materials science plays a pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry, influencing everything from vehicle performance and fuel efficiency to passenger safety and environmental impact. The continuous quest for lighter, stronger, and more sustainable materials drives innovation in vehicle construction, directly impacting how modern automobiles are designed, manufactured, and utilized globally. This fundamental discipline explores the properties and applications of various substances, enabling engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible in transportation.

The evolution of vehicles, from early carriages to today’s sophisticated automobiles, is inextricably linked to advancements in materials science. Engineers and designers constantly seek innovative materials that offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, enhanced durability, and improved environmental profiles. This pursuit not only enhances the driving experience but also contributes significantly to the overall sustainability and efficiency of the transport sector.
Materials for Enhanced Vehicle Safety
Safety remains a paramount concern in vehicle design, and materials science provides critical solutions. High-strength steels, often used in combinations with advanced aluminum alloys and composite materials, form the backbone of modern vehicle structures. These materials are engineered to absorb impact energy more effectively during collisions, protecting occupants. The strategic placement of different materials, such as ultra-high-strength steel in safety cages and crumple zones, is a direct result of extensive material research and simulation. This engineering ensures that vehicles can withstand significant forces while maintaining structural integrity for passenger compartments, thereby enhancing overall automotive safety.
Advancements in Materials for Electric Mobility
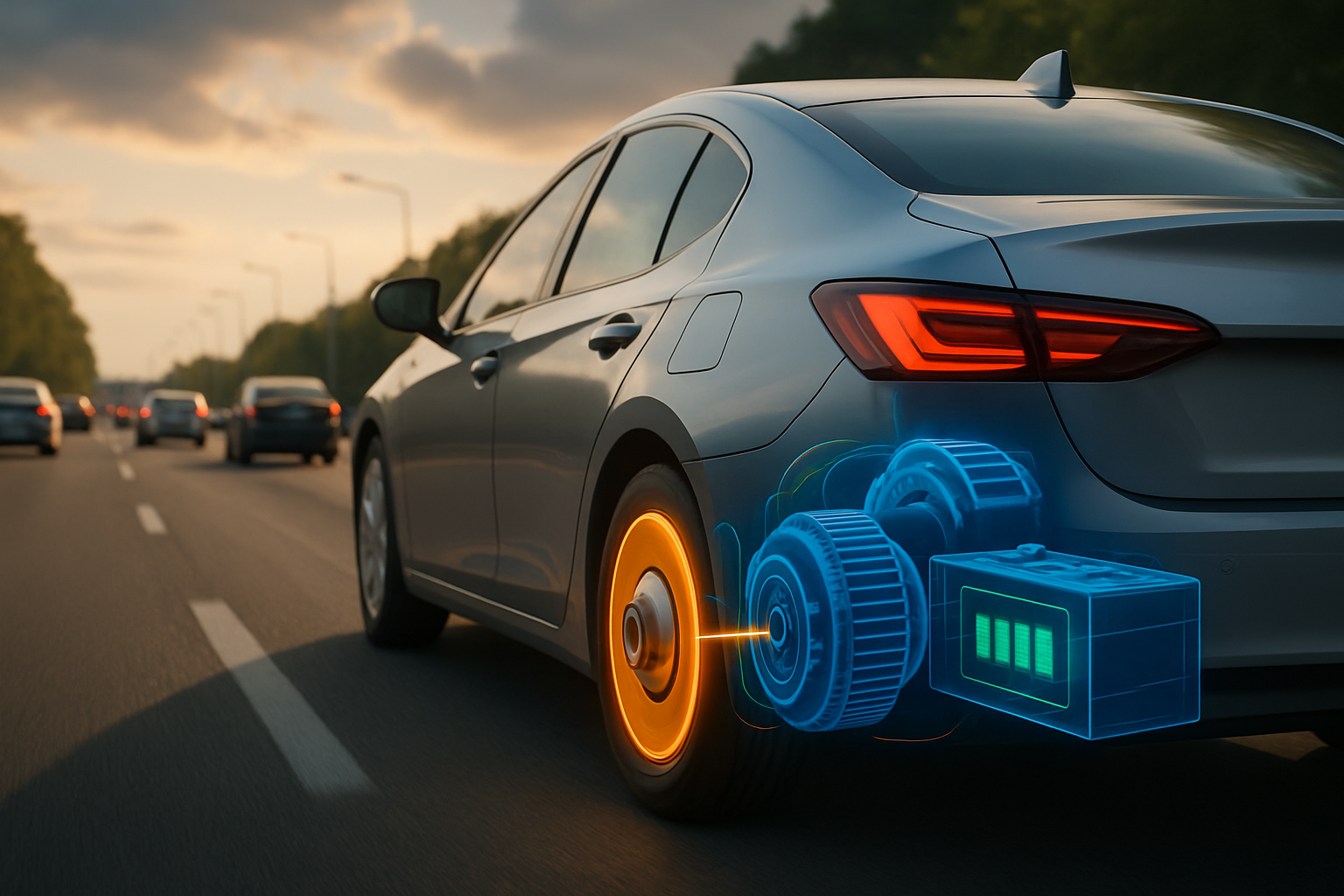
The shift towards electric mobility presents unique challenges and opportunities for materials science. Lightweight materials are crucial for electric vehicles (EVs) to maximize battery range and energy efficiency. Aluminum, magnesium alloys, and carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs) are increasingly used in EV body structures, chassis components, and battery enclosures. Beyond structural applications, advanced materials are vital for battery technology itself, including cathode and anode materials, electrolytes, and thermal management systems that ensure optimal battery performance and longevity. These material innovations are central to the future of electric transport.
Driving Automotive Innovation Through Material Design
Innovation in the automotive industry is often sparked by breakthroughs in material design. New materials enable engineers to create more complex shapes, integrate multiple functions into single components, and improve manufacturing processes. For instance, advanced polymers and composites allow for greater design freedom, enabling aerodynamic optimizations that contribute to better fuel economy and reduced noise. The development of smart materials, such as shape-memory alloys and self-healing coatings, also holds promise for future vehicle technologies, influencing automotive engineering and overall vehicle design.
Sustainable Materials in Vehicle Construction
The environmental impact of vehicle production and disposal is a growing concern, driving the automotive sector towards more sustainable practices. Materials science contributes by developing and incorporating recycled content, bio-based plastics, and natural fibers into vehicle components. Examples include interior trim made from recycled plastics, seat fabrics from sustainable sources, and sound-deadening materials derived from natural fibers. The goal is to reduce the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing, minimize waste, and enable easier recycling at the end of a vehicle’s life, aligning with a more sustainable future for transport.
Efficiency and Future Automotive Engineering
Material selection directly influences a vehicle’s efficiency, whether it’s a traditional internal combustion engine vehicle or an electric model. Lighter materials reduce the overall vehicle mass, requiring less energy for propulsion and improving fuel economy or extending EV range. Furthermore, advancements in materials for engines, transmissions, and electric motors contribute to greater operational efficiency and durability. The ongoing research into advanced ceramics, specialized alloys, and thermal barrier coatings is set to redefine what is possible in future automotive engineering, enabling more efficient and powerful propulsion systems. These developments are critical for the long-term efficiency of the global fleet and the future of driving.
Materials science encompasses a broad spectrum of substances, each with unique properties that can be leveraged in vehicle construction. Metals, such as various grades of steel (from mild to ultra-high-strength), aluminum, and magnesium, offer a balance of strength, ductility, and weight. Composites, including carbon fiber and glass fiber reinforced plastics, provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for high-performance applications and weight reduction. Polymers, ranging from durable plastics used in interiors to specialized elastomers for seals and tires, contribute to comfort, aesthetics, and functionality. The strategic combination and application of these diverse material categories are fundamental to meeting the evolving demands of modern vehicles, from robust chassis to intricate electronic components, influencing every aspect of a vehicle’s life cycle.
The profound influence of materials science on vehicle construction cannot be overstated. It is a dynamic field that continuously introduces new possibilities for enhancing safety, improving efficiency, fostering sustainable practices, and enabling the cutting-edge technologies that define modern and future vehicles. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, driven by demands for better performance, reduced environmental impact, and advanced features, materials science will remain at the forefront of innovation, shaping the next generation of transport solutions worldwide.