The Peculiar World of Axolotl Regeneration
In the realm of extraordinary creatures, few can match the awe-inspiring abilities of the axolotl. These aquatic salamanders, native to Mexico, possess an unparalleled talent for regeneration that has captivated scientists and animal enthusiasts alike. From regrowing limbs to repairing vital organs, axolotls showcase nature's remarkable capacity for self-healing.

A Glimpse into Axolotl Biology
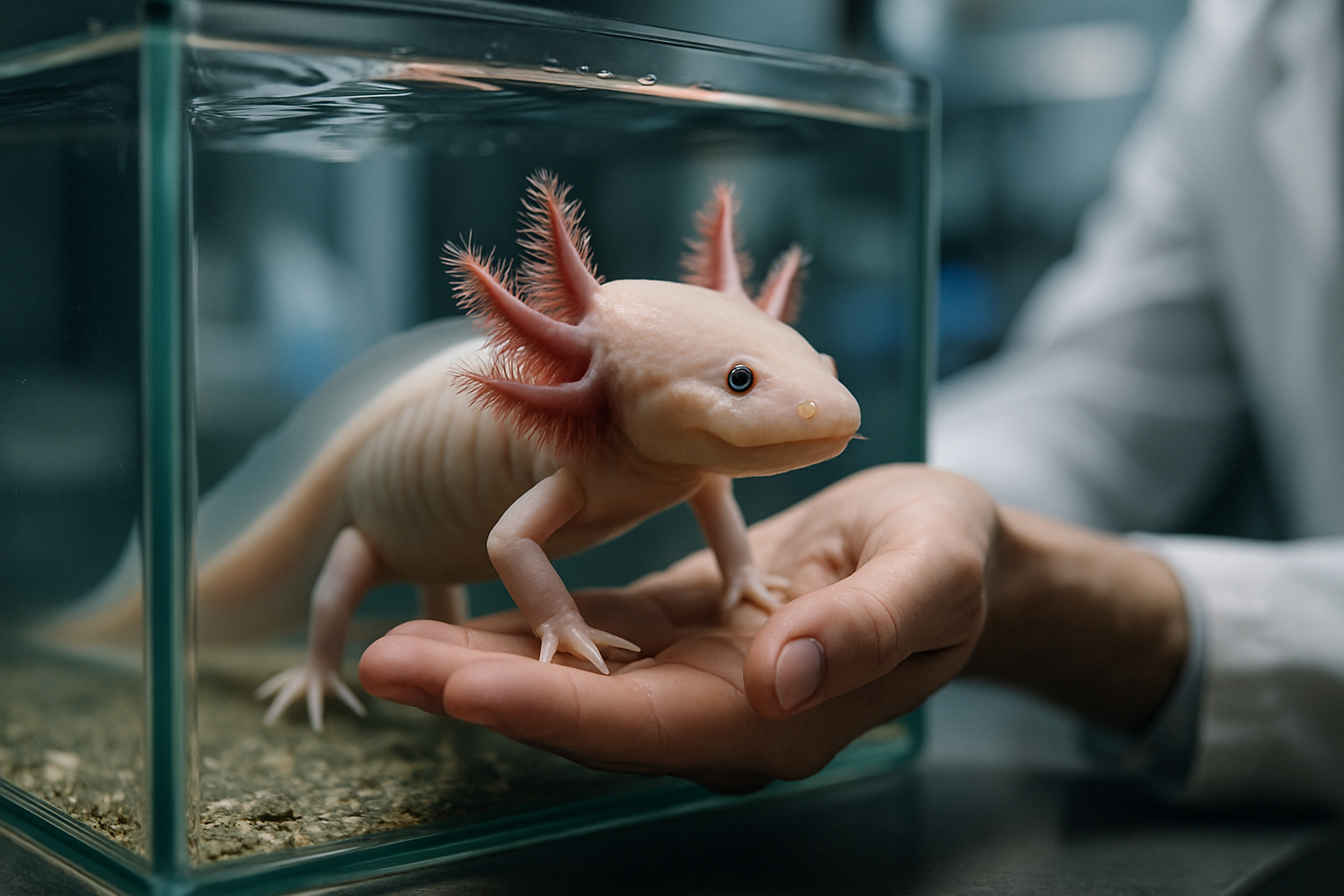
Axolotls are neotenic salamanders, meaning they retain juvenile features throughout their lives. They possess external gills, a tadpole-like dorsal fin, and a distinctively flat head. Their natural habitat is limited to Lake Xochimilco and other water bodies near Mexico City, where they are now critically endangered due to urbanization and pollution.
These unique creatures typically reach lengths of 15 to 45 centimeters and can live up to 15 years in captivity. Their most striking feature, however, is not their appearance but their incredible regenerative abilities. Unlike most other animals, axolotls can regrow entire lost limbs, including bones, muscles, and nerves, within weeks.
The Science Behind Regeneration
The secret to axolotl regeneration lies in their ability to dedifferentiate and redifferentiate cells. When an axolotl loses a limb, the cells at the site of injury revert to a stem cell-like state. These cells then multiply and specialize again to form the various tissues needed to rebuild the lost appendage.
This process is governed by a complex interplay of genes and signaling molecules. Recent studies have identified key genes involved in axolotl regeneration, including those responsible for producing fibroblast growth factors and other crucial proteins. Understanding these mechanisms could potentially lead to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine for humans.
Implications for Human Medicine
The axolotl’s regenerative abilities have significant implications for human medicine. Researchers are studying these creatures in hopes of unlocking the secrets to tissue regeneration in humans. While we are far from being able to regrow limbs, insights from axolotl research could lead to improved treatments for spinal cord injuries, heart damage, and other conditions that currently have limited therapeutic options.
One area of particular interest is the axolotl’s ability to regenerate brain tissue. Unlike humans, axolotls can repair damaged areas of their brain without losing memories or cognitive function. This has led scientists to investigate whether similar mechanisms could be activated in human brains to treat neurodegenerative diseases or brain injuries.
Axolotls in Captivity
The unique abilities of axolotls have made them popular in the pet trade, with enthusiasts around the world keeping them in home aquariums. While they can make fascinating pets, their care requires specific knowledge and dedication. Axolotls need cool, clean water with minimal water movement, a diet of live or frozen foods, and protection from bright light.
The price of an axolotl can vary widely depending on factors such as color morph and availability. Common varieties may cost between $20 and $70, while rare color morphs can fetch prices upwards of $200. The market for axolotls has seen steady growth in recent years, driven by increased interest in exotic pets and the creatures’ unique biological features.
Conservation Challenges
Despite their popularity in captivity, wild axolotls face severe threats to their survival. Their natural habitat in Mexico has been drastically reduced due to urban expansion, water pollution, and the introduction of invasive species. It’s estimated that fewer than 1,000 axolotls remain in the wild, making them critically endangered.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect the remaining wild populations and their habitat. These include projects to improve water quality in Lake Xochimilco, captive breeding programs, and educational initiatives to raise awareness about the importance of axolotl conservation. The survival of these remarkable creatures in their natural habitat is crucial not only for biodiversity but also for the potential scientific breakthroughs their unique abilities may unlock.
Ethical Considerations in Axolotl Research
As research on axolotls continues to advance, ethical considerations have come to the forefront. While the potential benefits to human medicine are significant, there are concerns about the welfare of axolotls used in scientific studies. Researchers must balance the pursuit of knowledge with the ethical treatment of these sentient creatures.
Efforts are being made to develop alternative research methods that minimize harm to axolotls. These include advanced imaging techniques that allow for non-invasive study of regeneration processes and the development of 3D-printed axolotl limbs for preliminary experiments. Such innovations aim to reduce the number of live animals needed for research while still advancing our understanding of regeneration.
The Future of Axolotl Research
The field of axolotl research is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries continually expanding our understanding of regeneration. Recent advances in gene editing technologies like CRISPR have opened up new avenues for investigating the genetic basis of axolotl regeneration. By selectively modifying genes, researchers can gain insights into which genetic factors are crucial for regenerative processes.
Looking ahead, the integration of axolotl research with other fields such as tissue engineering and stem cell biology holds promise for translational applications. While we may be years away from replicating axolotl-like regeneration in humans, each step forward brings us closer to developing new therapies for previously untreatable conditions.
Conclusion
The axolotl’s extraordinary regenerative abilities continue to astound and inspire scientists and animal enthusiasts alike. From their unique biology to their potential impact on human medicine, these remarkable creatures offer a window into nature’s most impressive healing mechanisms. As research progresses and conservation efforts intensify, the axolotl stands as a testament to the wonders of the natural world and the boundless potential of scientific discovery.