Decoding Elephant Rumbles: The Low-Frequency Language of Giants
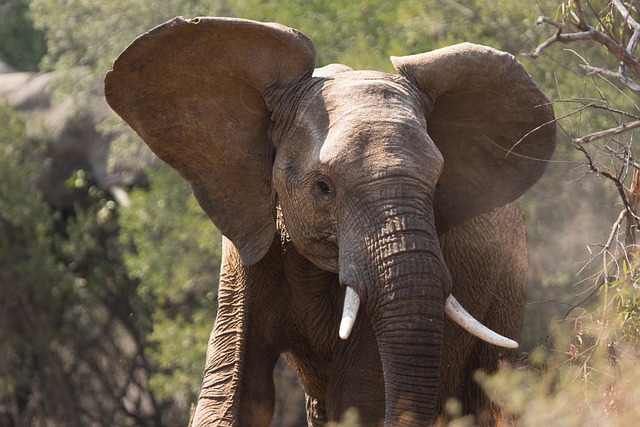
Elephants, nature's gentle giants, have long captivated our imagination with their intelligence and social complexity. But beneath their thunderous footsteps lies a hidden world of communication that's only recently come to light. These majestic creatures use infrasonic rumbles - sounds so low-pitched that humans can't hear them - to convey messages across vast distances. This article delves into the fascinating realm of elephant vocalizations, exploring how these low-frequency rumbles shape elephant society and what they reveal about these remarkable animals.

This revelation opened up a new field of study, prompting researchers to develop specialized equipment to record and analyze these infrasonic vocalizations. The technology, initially priced at tens of thousands of dollars, has since become more accessible, allowing for more extensive research into this unique form of animal communication.
The Mechanics of Elephant Rumbles
Elephant rumbles are produced by the vibration of their massive vocal folds, which are nearly three times longer than those of humans. The size of these folds allows elephants to generate incredibly low-frequency sounds that can travel for miles through the air and ground. The elephants’ large nasal passages and trunk also play a crucial role in amplifying and directing these sounds.
Interestingly, elephants can both produce and perceive these low-frequency vocalizations. Their ears are specially adapted to detect infrasonic waves, and they can even sense vibrations through their feet and trunk. This multi-sensory reception allows elephants to gather information from their environment in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
The Language of Rumbles
Elephant rumbles serve a variety of purposes within their complex social structures. These vocalizations can convey information about an individual’s identity, emotional state, and reproductive status. For instance, females in estrus produce distinct rumbles that attract potential mates from great distances, sometimes up to 10 kilometers away.
Rumbles also play a crucial role in maintaining social bonds within elephant herds. Mothers and calves use low-frequency calls to stay in contact, even when separated by dense vegetation or large distances. Additionally, rumbles help coordinate group movements and warn of potential dangers, such as the presence of predators or human threats.
Decoding Elephant Emotions
Recent studies have shown that elephant rumbles contain a wealth of emotional information. By analyzing the acoustic properties of these vocalizations, researchers can now identify different emotional states in elephants, including excitement, fear, and distress. This breakthrough has significant implications for elephant conservation and welfare, as it allows for better assessment of their psychological well-being in both wild and captive environments.
The estimated cost of equipment used in these studies ranges from $5,000 to $50,000, depending on the sophistication of the recording and analysis tools. Despite the high cost, this research has had a significant impact on our understanding of elephant behavior and has influenced conservation strategies worldwide.
Implications for Conservation
Understanding elephant infrasonic communication has become a vital tool in conservation efforts. By monitoring these vocalizations, researchers can track elephant movements, assess population dynamics, and identify potential conflicts with human settlements. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and mitigating human-elephant conflicts.
Moreover, the study of elephant rumbles has led to the development of innovative deterrent systems that use low-frequency sounds to guide elephants away from crops and human habitations. These non-invasive methods, which respect the elephants’ natural communication patterns, offer a promising alternative to more traditional and often harmful deterrent techniques.
Challenges in Studying Infrasonic Communication
Despite significant advancements, researching elephant infrasound presents unique challenges. The low-frequency nature of these vocalizations makes them susceptible to interference from environmental noise, including wind and human-generated sounds. Researchers must continually refine their recording techniques and analysis methods to accurately capture and interpret these subtle signals.
Additionally, the vast ranges over which elephants communicate make it difficult to study their vocalizations comprehensively. Scientists often need to deploy multiple recording stations across large areas, which can be logistically challenging and expensive.
Future Directions in Elephant Communication Research
As technology continues to advance, so does our ability to study and understand elephant infrasonic communication. Emerging research is exploring the potential for machine learning algorithms to automatically detect and classify elephant vocalizations, which could revolutionize long-term monitoring efforts.
Scientists are also investigating the possibility that elephants use seismic vibrations - traveling through the ground rather than the air - as an additional communication channel. This exciting avenue of research may reveal even more complexity in elephant social interactions and spatial awareness.
Conclusion: The Resonating Impact of Elephant Rumbles
The discovery and ongoing study of elephant infrasonic communication have profoundly altered our perception of these magnificent animals. As we continue to unravel the intricacies of their low-frequency language, we gain not only a deeper appreciation for their intelligence and social complexity but also valuable insights that can aid in their conservation.
From coordinating herd movements to expressing emotions, elephant rumbles form the backbone of a sophisticated communication system that has evolved over millions of years. By listening to these inaudible conversations, we’re learning to speak the language of giants, fostering a deeper connection with one of Earth’s most iconic species.